Parkinson’s Disease in Older Adults: Challenges and Care
Table Of Contents
- 1 Global Statistics: Impact and Prevalence of Parkinson's Disease
- 2 Detailed Overview: Effects of Parkinson's Disease on Daily Life
- 3 Parkinson's Symptoms: Breakdown of Physical and Cognitive Manifestations
- 4 Motor Symptoms:
- 5 Non-Motor Symptoms:
- 6 Additional Challenges:
- 7 Diagnosis and Global Burden: Addressing Parkinson's Disease
- 8 Current Treatments: Management and Advances in Parkinson's Disease
- 9 Caregivers and Families: Challenges and Support in Parkinson's Disease
- 10 Rights and Challenges: Combating Discrimination in Parkinson's Disease
- 11 Navigating Toward Quality of Life in Old Age with Comprehensive Support
The growing prevalence of Parkinson’s disease among the global population of older adults poses an unparalleled challenge. In this article, we aim not only to understand but also to highlight the complexity of this condition, demanding increasingly urgent attention. We will guide readers from the fundamentals to the intricate web of diagnoses and treatments, immersing ourselves in the fascinating journey of comprehending and addressing this reality that affects so many in the golden stage of their lives.
Global Statistics: Impact and Prevalence of Parkinson's Disease
Globally, rates of disability and mortality linked to Parkinson’s disease are on the rise, showing a significant increase in the last five years. This trend is observed not only worldwide but also in countries like the United States. With a 15% increase in the prevalence of the disease, affecting approximately 2% of the population, and a 10% rise in deaths in the last decade, accounting for 1.5% of total fatalities, the figures paint a striking picture.
Despite advancements, crucial challenges persist, especially in access to essential treatments such as levodopa/carbidopa, affecting around 20% of those affected. These statistics are not just numbers; they represent individuals and communities facing a complex reality. In this context, primary care, supported by simplified clinical diagnoses, emerges as a vital strategy to improve disease management. For more details and to support these statistics, we invite you to explore the official WHO website (https://www.who.int/en), which backs the shared data.
Detailed Overview: Effects of Parkinson's Disease on Daily Life
Parkinson’s disease, a neurodegenerative movement disorder, profoundly impacts daily life and the quality of life for those affected. Beyond the physical challenges, the disease also affects mental health, giving rise to issues such as depression, anxiety, and cognitive difficulties. This complex panorama is exacerbated by disruptions in sleep patterns, creating a significant burden in everyday life.
As the disease progresses over time, individuals experience a gradual decline in their quality of life. Although there is no definitive cure, various treatments and medications are designed to alleviate associated symptoms. These symptoms range from noticeable tremors to difficulties in verbal expression, encompassing a wide array of physical and emotional challenges. We will delve into this diversity of symptoms and how the disease affects both older individuals and, at times, younger ones.
Parkinson's Symptoms: Breakdown of Physical and Cognitive Manifestations
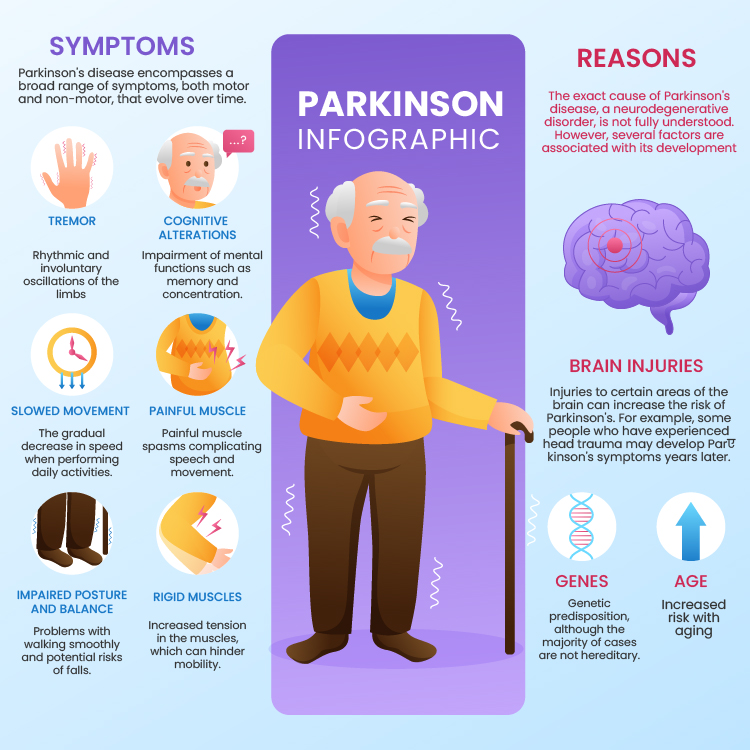
Parkinson’s disease encompasses a broad range of symptoms, both motor and non-motor, that evolve over time. These symptoms can significantly affect the quality of life for those affected. The following are some of the most prominent symptoms:
Motor Symptoms:
- Slowness of Movements (Bradykinesia): The gradual decrease in speed when performing daily activities.
- Tremors (Resting Tremor): Rhythmic and involuntary oscillations of the limbs, especially at rest.
- Involuntary Movements (Dyskinesias): Abnormal, often impulsive and uncontrolled movements.
- Muscle Stiffness: Increased tension in the muscles, which can hinder mobility.
- Difficulty Walking and Loss of Balance: Problems with walking smoothly and potential risks of falls.
Non-Motor Symptoms:
- Cognitive Alterations: Impairment of mental functions such as memory and concentration.
- Sleep Disorders: Issues with falling or maintaining sleep, as well as deep sleep-related disorders.
- Pain: Painful sensations, often associated with muscle stiffness.
- Sensory Alterations: Changes in sensory perception, such as a decreased sense of smell.
Additional Challenges:
- Involuntary Movements (Dyskinesias): Uncontrolled oscillations that can interfere with daily activities.
- Painful Muscle Contractions (Dystonias): Painful muscle spasms complicating speech and movement.
Exploring these symptoms provides a more comprehensive understanding of the challenges faced by people with Parkinson’s disease. The comprehensive management of these symptoms is essential to improve the quality of life for those affected.

Diagnosis and Global Burden: Addressing Parkinson's Disease
The diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease goes beyond neurologists; the inclusion of non-specialized healthcare workers is key, especially in areas with limited neurological services. It highlights the importance of early intervention and primary care in improving patients’ quality of life. Globally, the prevalence has increased, with more than 2% of the adult population estimated to be affected, and a 15% increase in the United States in the last 10 years.
In 2019, the disease generated over 6 million disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), showing a significant 20% increase since 2000. The 350,000 deaths, representing a 25% increase, underscore the urgent need for effective interventions and public health policies.
Additionally, it is crucial to incorporate information on advances in diagnostic methods and treatment strategies that are making a difference. These developments can offer hope and improve disease management for those affected.
Current Treatments: Management and Advances in Parkinson's Disease
Although there is still no definitive cure for Parkinson’s disease, symptom management has advanced significantly thanks to various interventions. Chief among them is the use of medications, with levodopa/carbidopa being a key component by increasing dopamine levels in the brain, thereby alleviating motor symptoms.
However, it is crucial to stay updated on advances in research and treatment. Recent developments in medical science have shed light on new therapeutic options that could positively influence Parkinson’s disease management. Surgery, especially deep brain stimulation, has proven beneficial in controlling tremors and reducing dependence on certain medications.
Moreover, rehabilitation emerges as a fundamental pillar in this comprehensive approach. Physical therapy, in particular, plays a crucial role in improving mobility, strengthening muscles, and addressing the physical challenges associated with the disease. Strength training, mobility and balance exercises, as well as hydrotherapy, are presented as effective options to enhance the quality of life.
This comprehensive approach aims not only to alleviate symptoms but also to empower the independence and overall well-being of those facing Parkinson’s disease. Stay informed about ongoing medical advances to ensure that treatment options are the most up-to-date and beneficial for patients.
Caregivers and Families: Challenges and Support in Parkinson's Disease
Informal caregivers, commonly friends and family, face a substantial burden by dedicating extensive daily hours to the care of those affected by Parkinson’s disease. This unwavering commitment, though noble, can lead to the recognized caregiver syndrome, a condition that impacts the physical and mental health of those taking on this responsibility.
Physical stress manifests through the physical demands associated with daily assistance, while the resulting emotional burden of seeing a loved one face the disease can lead to mental exhaustion. Additionally, economic implications, such as medical expenses and the potential need to reduce working hours, add additional pressure on informal caregivers.
It is vital to highlight the importance of effective support systems. Residences like Villa Alegría provide specialized environments that not only address the needs of the patient but also offer support for caregivers. Additionally, programs like WHO’s iSupport provide practical and emotional guidance while fostering the creation of support networks among those facing similar challenges.
Recognizing and addressing the impact on families and caregivers is essential to build a strong support network that improves the quality of life for both those facing Parkinson’s disease and those dedicating their efforts to daily care.
Rights and Challenges: Combating Discrimination in Parkinson's Disease
Older individuals facing Parkinson’s disease are often affected by stigma and discrimination. This challenge manifests as unfair discrimination in the workplace and limited social participation. Addressing and overcoming these myths and obstacles is essential to ensure equity in access to health services.
In response to these challenges, the World Health Assembly, in May 2022, approved a Global Intersectoral Action Plan on Epilepsy and Other Neurological Disorders. This global plan prioritizes policies, governance, effective diagnostics, prevention strategies, research, and innovation to improve care for older people with Parkinson’s disease.
Navigating Toward Quality of Life in Old Age with Comprehensive Support
In the landscape of Parkinson’s disease in older adults, the WHO technical report, “Parkinson’s Disease: A Public Health Approach,” stands out as an essential guide. Directed at regulators, managers, and healthcare providers, it identifies critical areas of action to improve the quality of life for older adults facing Parkinson’s disease.
As we seek valuable resources, specialized centers like Villa Alegría emerge as crucial pillars in the comprehensive care of older adults with Parkinson’s, ensuring excellence and quality. Beyond providing specialized care, these centers act as support communities, contributing significantly to a better quality of life in the fight against Parkinson’s disease in old age.
19 thoughts on “Parkinson’s Disease in Older Adults: Challenges and Care”
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Thank you for the auspicious writeup. It in fact was a amusement account it.
Look advanced to far added agreeable from you!
However, how can we communicate?
Thank you for your kind words! We’re glad to hear that you enjoyed the content. If you have any questions or would like to communicate further, feel free to reach out through the contact information provided on our website. We’re here to help and look forward to hearing from you. villalegria@nursinghomescostarica.com
Thank you for writing this post!
Your articles are extremely helpful to me. Please provide more information!
Thank you! The next post will be about Parkinson’s disease. Stay tuned for valuable insights!
The articles you write help me a lot and I like the topic
Thank you! Your feedback means a lot to us!
You’ve the most impressive websites.
Thank you very much for your compliment! I’m glad you find the websites impressive. If you have any questions or need further assistance, feel free to reach out.
Thank you for sharing this article with me. It helped me a lot and I love it.
You’re welcome! I’m glad to hear that the article was helpful to you and that you enjoyed it.
Your articles are extremely helpful to me. Please provide more information!
I’m delighted to hear that you find the articles helpful! I’ll make sure to provide you with more information. Stay tuned for updates!
You helped me a lot by posting this article and I love what I’m learning.
I’m glad to hear that the article has been helpful to you and that you’re enjoyi
Sustain the excellent work and producing in the group!
Thank you for the encouraging words! We’re committed to delivering valuable content and appreciate your support. If you have any specific topics or questions you’d like us to cover, feel free to let us know. Stay tuned for more insightful articles!
I simply couldn’t leave your website before suggesting that I really enjoyed the
usual info an individual provide for your visitors?
Is gonna be again continuously to check up on new posts
I’m delighted to hear that you enjoyed exploring our website! We’re committed to providing valuable and engaging content. Feel free to visit regularly for the latest updates and new posts. If there’s anything specific you’d like to see more of, let us know. Thank you for your continuous support!